
Panel physician will provide Pre- and post-test counselling to explain the following
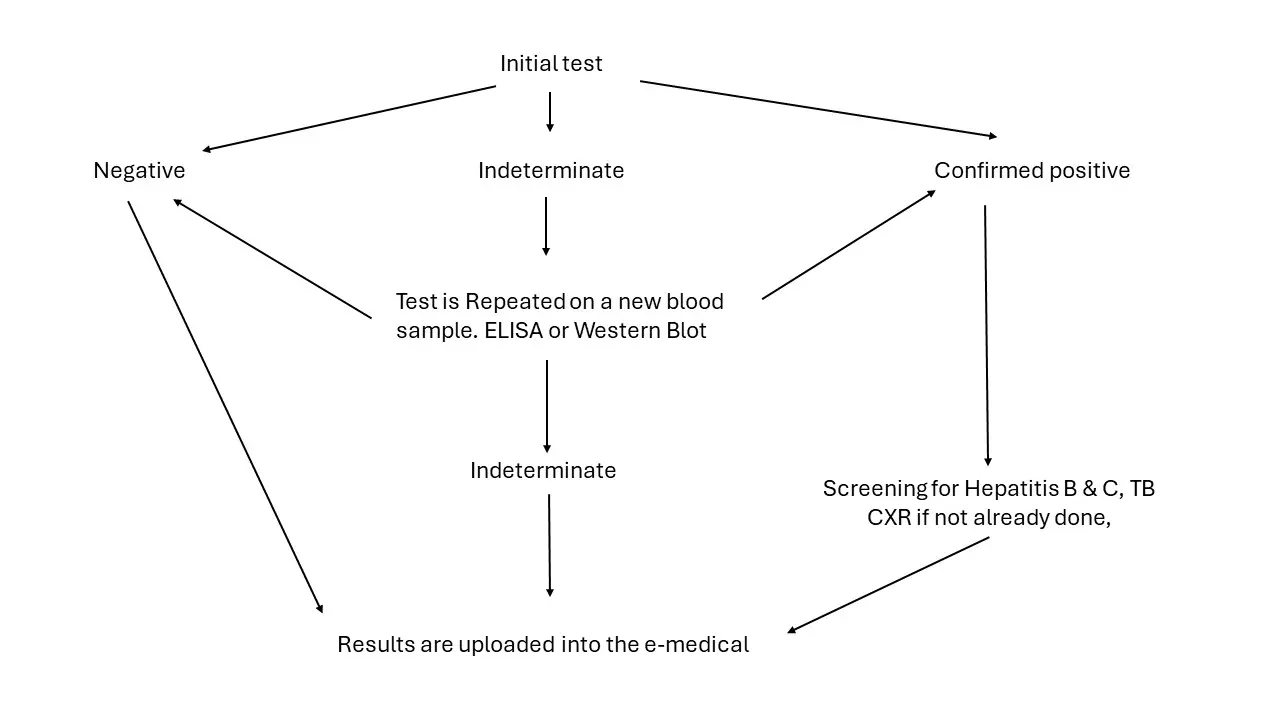
1. Initial Test:
2. Discordant Results:
3. Indeterminate Results:
4. Post-Test Process:

For an applicant with a confirmed positive HIV result, the following information may be required:
If this is a new HIV diagnosis or the applicant is not currently on antiretroviral therapy, the RMO may request an HIV Expert report from a specialist or a physician knowledgeable in HIV treatment.